
5.4 Comparative assessment of the fungicidal activity of preparations and their effect on the pathogenic microfungi of spring wheat
The vegetation seasons of 2024 differed in various weather conditions, and at certain periods, they were unfavourable for the growth and development of spring wheat cultivated in the North-East of Kazakhstan. The air temperature during the wheat vegetation mostly exceeded the long-term average indicators, with a significant moisture deficit. Such climatic conditions during the vegetation period of spring wheat were favourable for the spread of phytopathogens and the development of fungal diseases in the research agrocenoses. The plants of spring wheat during the monitoring period experienced stress conditions in terms of daily temperatures, soil, and air humidity, as well as the pathological effects of phytopathogens.
Spring wheat was infected with powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis), leaf brown rust (Puccinia triticina), and septoria leaf blotch (Septoria sp.). Powdery mildew intensity of manifestation was around 30%, rust intensity - 15%, and septoria leaf blotch intensity - 25% prior to the use of fungicides (during the stage of flag leaf emergence). The intensity of disease manifestation was considerably reduced in 10 days after fungicide application: powdery mildew by 75.1-90.1%, rust by 55.2-61.7%, and septoria leaf blotch by 35.1-48.6%. At the same time, Rex Duo fungicide was the most effective against the disease complex. After 20 days, Rex Duo completely suppressed powdery mildew, reduced leaf rust manifestation by 78.7% and septoria leaf blotch by 71.4%. By this time, the intensity of powdery mildew manifestation had dropped to 17.0% due to the action of abiotic factors (untreated region), but the same indicators of leaf rust and septoria leaf blotch had reached their maximum values (43.9% and 88.8%) (Table 5, Figures 31, 32).
Table 5 - Biological efficiency of fungicides (flag leaf emergence)
|
Option |
Biological efficiency against disease, % |
|||||
|
Powdery mildew |
Powdery mildew |
Powdery mildew |
||||
|
10 days |
10 days |
10 days |
10 days |
10 days |
10 days |
|
|
Kolosal Pro, 0,6 l/ha |
75,1 |
91,2 |
51,3 |
66,9 |
34,1 |
60,9 |
|
Rex Duo, 0,5 l/ha |
90,1 |
100 |
62,1 |
78,6 |
47,5 |
71,5 |
|
Varro, CS, 0,25 l/ha |
84,9 |
97,9 |
57,4 |
70,0 |
45,3 |
67,3 |
|
Control |
26,5 |
17,1 |
17,6 |
43,9 |
27,5 |
88,8 |
|
LSD0,5 |
3,2 |
4,9 |
4,0 |
2,7 |
5,4 |
2,8 |
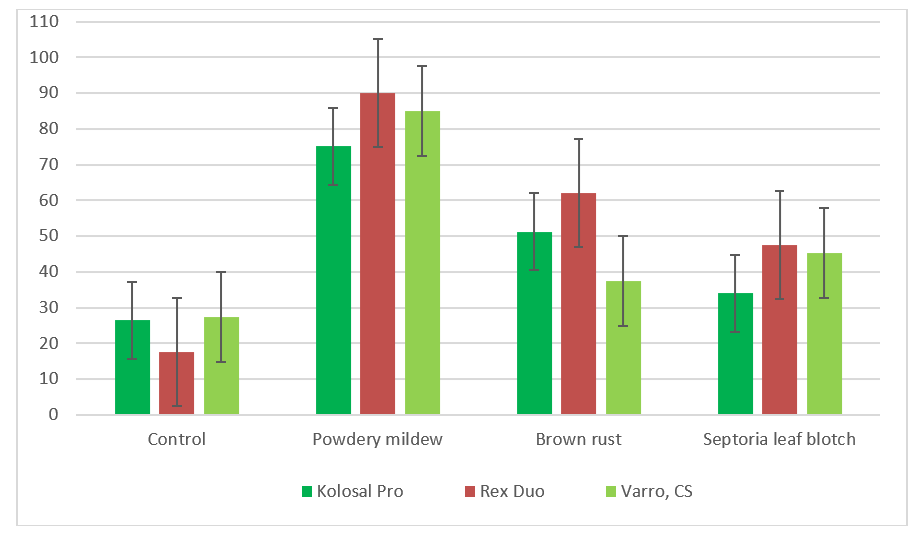
Figure 31 - Biological efficiency of fungicide application after 10 days
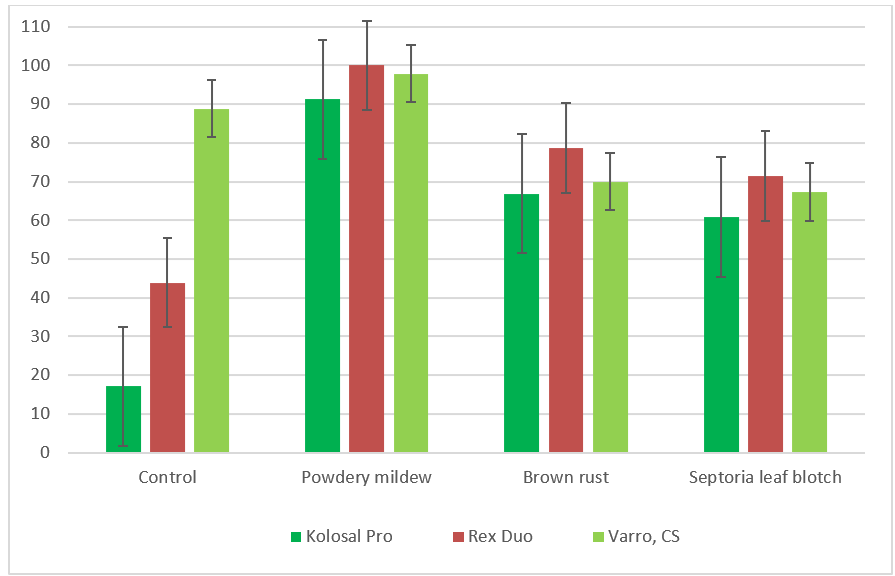
Figure 32 - Biological efficiency of fungicide application after 20 days
As a result of the research, it was established that fungicides have an influence on growth and productive processes during the vegetation of crops. The use of the fungicide Rex Duo, along with foliar fertilisation with ammonium nitrate N34 in different phases of crop vegetation, significantly improved the indicators of spring wheat plant condition. There was an increase in the number of productive stems, plant height, and number of grains per spike, as well as the weight of 1000 grains (Table 6).
Table 6 - Plant indicators when using fungicides during the vegetation of spring wheat in the flag leaf stage (37-39)
|
Option |
Indicators |
|||||
|
Productive stems, pcs/m2 |
Plant height, cm |
Grain number per ear, pcs |
Weight of grains per ear, g |
Weight of 1000 grains, g |
Biological yield, centner/ha |
|
|
Kolosal Pro, 0,6 l/ha |
393 |
97,0 |
25,2 |
0,932 |
36,6 |
36,5 |
|
Rex Duo, 0,5 l/ha |
394 |
98,3 |
27,8 |
1,092 |
39,5 |
42,8 |
|
Varro, CS, 0,25 l/ha |
391 |
98,3 |
25,8 |
0,985 |
38,1 |
38,5 |
|
Control |
392 |
95,3 |
25,1 |
0,883 |
35,0 |
34,6 |
|
LSD0,5 |
4,9 |
2,1 |
1,6 |
0,13 |
1,2 |
1,3 |
These fertilisation methods were particularly effective during the tillering and heading phases. The research showed that the biological yield without any fertilisation or fungicide application was 38.9 c/ha, while with only the fungicide, it increased to 43.4 c/ha. A single foliar fertilisation with ammonium nitrate during the tillering phase, followed by the application of the fungicide-based product during the flag leaf phase, increased the biological yield to 52.7 c/ha. Furthermore, using two foliar fertilisations (during tillering and heading phases) resulted in the highest experimental biological yield of 60.9 c/ha (Table 7).
Table 7 - Plant indicators of spring wheat when applying fungicides on the background of nitrogen fertilisers
|
Option |
Indicators |
|||||
|
Productive stems, pcs/m2 |
Plant height, cm |
Grain number per ear, pcs |
Weight of grains per ear, g |
Weight of 1000 grains, g |
Biological yield, centner/ha |
|
|
Ammonium nitrate N34 (tillering stage) + Rex Duo 0.5 l/ha (flag leaf stage) |
413 |
107,4 |
29,1 |
1,275 |
44,1 |
52,7 |
|
Ammonium nitrate N34 (tillering stage) + N34 + Rex Duo 0.5 l/ha (ending of stem elongation stage) + N34 (heading stage) |
421 |
112,8 |
31,2 |
1,448 |
46,8 |
60,9 |
|
Rex Duo 0.5 l/ha (ending of stem elongation stage) |
389 |
104,2 |
27,8 |
1,115 |
40,1 |
43,4 |
|
Control |
390 |
99,1 |
26,8 |
0,997 |
36,9 |
38,9 |
|
LSD0,5 |
6,5 |
4,9 |
2,2 |
0,22 |
2,1 |
2,9 |
In agrocenoses of spring wheat under conditions unfavourable for crop development but favourable for disease manifestation and spread, the fungicide Rex Duo at a normal consumption rate of 0.5 l/ha effectively suppressed powdery mildew. It reduced the prevalence of the disease from 100% to 18-20% on the 12th day after application and decreased the intensity of its manifestation from 45% to 5%. The biological effectiveness of the fungicide, calculated based on the degree of powdery mildew development, reached 88-89% during this period. On the 22nd day after application, the prevalence of powdery mildew was reduced to 4-5% compared to 100% in the control, and the intensity of the disease decreased from 60% in the control to 3% in the treated fungicide variants. The biological effectiveness on the 22nd day after treatment against powdery mildew was 92-95% (Table 8).
The fungicidal activity of the product on spring wheat was moderate against leaf rust. After 12 days, the prevalence in the treated variants was 13-14% compared to 60% in the control, and the degree of disease development was 10% compared to 25% in the control. The biological effectiveness during this period ranged from 60% to 64%.
Table 8 - Plant indicators of spring wheat when using fungicides on the background of nitrogen fertilisers and the growth regulator Binoram
|
Disease manifestation |
Options |
||||||||
|
Rex Duo 0.5 l/ha + Binoram |
Rex Duo 0.5 l/ha |
Control |
|||||||
|
Before treatment |
After 12 days |
After 22 days |
Before treatment |
After 12 days |
After 22 days |
Before treatment |
After 12 days |
After 22 days |
|
|
Powdery mildew |
|||||||||
|
Disease prevalence, % |
100 |
18 |
4 |
100 |
20 |
5 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
Degree of development, % |
30 |
5 |
3 |
30 |
5 |
3 |
30 |
45 |
60 |
|
Biological efficiency, % |
- |
89 |
95 |
- |
88 |
92 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Brown rust |
|||||||||
|
Disease prevalence, % |
50 |
13 |
12 |
60 |
14 |
13 |
50 |
60 |
70 |
|
Degree of development, % |
15 |
10 |
8 |
15 |
10 |
8 |
15 |
25 |
45 |
|
Biological efficiency, % |
- |
64 |
84 |
- |
60 |
80 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Septoria leaf blotch |
|||||||||
|
Disease prevalence, % |
45 |
28 |
20 |
45 |
30 |
23 |
45 |
60 |
90 |
|
Degree of development, % |
25 |
20 |
15 |
25 |
20 |
15 |
25 |
35 |
50 |
|
Biological efficiency, % |
- |
45 |
60 |
- |
40 |
50 |
- |
- |
- |
After 22 days of treatment, the prevalence of brown rust increased to 70% in the control plot, while it was significantly reduced to 12-13% in the treated plots. The degree of disease development reached 45% in the control plot, but only 8% in the treated variants. The biological effectiveness of Rex Duo against brown rust in spring wheat was 80-84% after 22 days.
The fungicidal effect of the product on spring wheat was less expressed against septoria leaf spot. After 12 days, the prevalence in the treated variants was 28-30% compared to 60% in the control, and the degree of disease development was 20% compared to 35% in the control. The level of biological effectiveness during this period was 40-45%. After 22 days of treatment, the prevalence of septoria leaf spot increased to 90% in the control plot, while it was relatively lower at 20-23% in the treated plots. The degree of disease development reached 60% in the control plot, but only 15% in the treated variants. The biological effectiveness of Rex Duo against septoria leaf spot in spring wheat after 22 days of treatment was 50-60%.
The additional use of the growth stimulator Binoram during crop vegetation slightly increased the effectiveness of the fungicide.