
CHAPTER 14. PUBLIC POLICY IN THE CONTEXT OF GLOBALIZATION AND CRISES
14.1 Globalization and public policy.
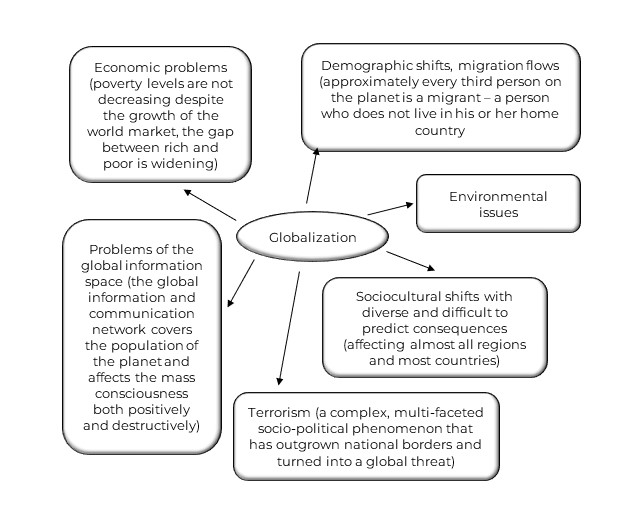
Globalization has become a key concept that characterizes the processes of world development in the XXI century. Its essence is a sharp expansion and complication of the interrelations and interdependencies of both people and States, which is reflected in the processes of formation of the planetary information space, the global market of capital, goods and labor, the internationalization of problems of man-made impact on the natural environment, interethnic and inter-confessional conflicts and security.
In modern conditions, the phenomenon of globalization covers almost all spheres of social activity, including politics, ideology, culture, way of life, as well as the very conditions of human existence.
The prerequisites for globalization processes were the information revolution, which provides the technical basis for creating global information networks, the internationalization of capital and the tightening of competition in world markets, the shortage of natural resources and the intensification of the struggle for control over them, the demographic explosion, as well as the increased technological burden on nature and the distribution of weapons of mass destruction, which increases the risk of a general catastrophe. These facts, despite their heterogeneity, are closely related to each other, and their interaction determines the complex and contradictory nature of globalization processes.
Information technologies create a real opportunity to dramatically accelerate the economic, scientific and cultural development of the planet, to unite humanity in a community that is aware of its interests and responsibility for the fate of the world. They can also become tools for dividing the world and intensifying confrontation.
So, globalization is the merging of national economies into a single, global system based on a new ease of movement of capital, a new information openness of the world, a technological revolution, the commitment of developed industrial countries to liberalize the movement of goods and capital, on the basis of communication convergence, a planetary scientific revolution, international social movements, new modes of transport, implementation of the telecommunications technologies, international education[200].
Thus, globalization is understood as the gradual transformation of the world space into a single zone, where capital, goods, and services move freely, where ideas are freely distributed and their carriers move, stimulating the development of modern institutions and polishing the mechanisms of their interaction. Globalization creates an international legal, cultural and informational field, a kind of infrastructure for inter-regional and information exchanges.
Globalization is designed to give the world community a new quality, and understanding this process will allow people to better navigate the era of innovative technologies.
The main features of globalization are:
- increasing global inequality. There is an obvious marginalization of developing countries – the rich North essentially excludes the vast majority of humanity from progress;
- excluding entire societies from the process of global modernization increases the risk of ethnic and national conflicts, terrorism, and armed conflicts;
- developed countries transfer pollutants for disposal to poor countries, turning them into landfills of substances harmful to health[201].
The transition from an industrial society to an information society, to high technologies
Transition from centralization of the economy to its decentralization
Transition from alternative choice to diversity of choice
Transition from national to global economy
Use of new communication technologies
Scheme 14.1.1 – Main causes of globalization
Globalization is a process of global economic, political and cultural integration and unification. The main consequence of this is the global division of labor, migration (and, as a rule, concentration)of capital, human and productive resources in the global headquarters, standardization of legislation, economic and technological processes, convergence and merging of cultures of different countries. This is an objective process that is systematic in nature, that is, it covers all spheres of society's life. As a result of globalization, the world is becoming more connected and dependent on all its subjects. There is both an increase in the number of problems common to a group of States and an expansion in the number and scope of integrating entities. This process connects all aspects of the life of national societies in a single world system. The importance of national and international interests is changing.
Globalization opens up unprecedented opportunities for prosperity for humanity and at the same time conceals colossal dangers that threaten the very existence of our civilization. Therefore, globalization and the ways of its development have become the subject of heated discussions. Social movements have emerged demanding that the negative consequences of this process be prevented.
It should be noted that hexalization is an objective regularity, and no forces can prevent its development. The task is to put it at the service of man. And this requires a significant increase in the level of governance of the international system in order to use the positive opportunities of globalization and prevent its negative consequences. In modern conditions, the problem of governance is a key global problem, and the resolution of other major problems depends on its solution. A significant obstacle to solving this problem is the lack of political thinking. One of the most important conditions for solving global problems, including the problem of governance, is to raise the level of political thinking and mass consciousness. Special responsibility for achieving this goal lies with the mass media, whose role in modern society has grown enormously. Without their active participation, effective governance is impossible at either the national or international level.
Globalization is a process of deepening economic, political, social and cultural ties between countries, which leads to an increase in the interdependence of States. In modern conditions, it has a significant impact on public policy, transforming national management strategies and regulating internal and external processes.
Characteristics of globalization:
- economic integration;
- information interconnectedness;
- multinational corporations.
The impact of global processes on national States: reduction of sovereignty, strengthening of international organizations.
Adaptation policy: economic liberalization, international treaties, cross-border cooperation.
The report of the World Commission on the Social Dimensions of Globalization states: «The behavior of nation states as global participants in the governance process is a factor that determines the quality of the entire global governance network. The degree to which they adhere to the ideas of multilateralism, universal values, common goals, their ability to respond to the inter – State consequences of their policies, and the importance they attach to global solidarity are all important factors that determine the quality of the global governance system. At the same time, the way they conduct their internal affairs has an impact on the extent to which people can benefit from globalization and be protected from its negative consequences. This premise reflects the fact that people live in nation states[202]».
The processes of globalization, such as international trade, migration, cultural exchanges and technological progress, affect the development of States, causing both positive and negative consequences. The study of the impact of globalization on the development of the state is an important aspect in the study of modern global problems and challenges faced by States.
The impact of globalization processes on the development of the state is characterized as twofold: on the one hand, globalization can stimulate economic and social growth, as well as contribute to improving international relations and integration into the world community. On the other hand, globalization can lead to various challenges and problems, such as increasing social inequality, limiting state sovereignty, worsening the environmental situation, and others.
The processes of globalization have a significant impact on the development of the state, and this impact is manifested in several aspects:
- economic dimension: globalization promotes international trade, investment, technology transfer and capital mobility. This can create new opportunities for the development of the state, but it can also cause problems in the form of competition, changes in economic relations and deterioration of living conditions for some social groups.
- political aspect: globalization contributes to the development of the international political system and the strengthening of relations between States. However, this can also cause problems associated with a decrease in the role of state borders and their sovereignty, as well as an increase in the influence of international institutions on the internal policy of the state;
- Social dimension: globalization affects the way of life of the population, including culture, education, health and social protection. This can lead to new opportunities and conditions for development, but it can also increase social inequality and worsen the quality of life for some population groups.
- ecological aspect: globalization can lead to a deterioration of the ecological situation in the state as a result of changes in economic relations, industrial activities, waste processing and the use of natural resources. This can cause problems with public health and environmental safety.
In general, the impact of globalization processes on the development of the state can have both positive and negative consequences. Therefore, it is important to take into account all aspects of the impact of globalization and develop strategies that will take advantage of its benefits and minimize its negative consequences[203].
Global processes and Kazakhstan.
Kazakhstan, as a country with a unique geographical location (at the junction of Europe and Asia), rich resource potential and a developing economy, is actively involved in global processes. Globalization, digitalization, international economic unions, environmental challenges and political transformation-all these factors have an impact on the country's public policy.
Globalization affects Kazakhstan in many areas:
- economic integration: participation in international organizations (WTO, EAEU, SCO), development of an expert-oriented economy;
- political cooperation: active diplomacy, participation in international peacekeeping missions;
- cultural influence: global brand distribution, digitalization, English-language education;
- social transformations: urbanization, growth of migration flows, changes in the structure of employment.
Kazakhstan is part of the global economy, exporting natural resources (oil, gas, uranium, metals) and promoting the non-resource sector. However:
- oil export tolerance makes the economy vulnerable to global commodity prices.
- diversification of the economy becomes a strategic task (development of agriculture, IT, mechanical engineering);
- WTO accession (2015) provided new opportunities, but increased competition for domestic producers.
Social processes in Kazakhstan under the influence of globalization.
Migration and urbanization: Kazakhstan is experiencing a «brain drain» – qualified specialists leave for developed countries, an increase in internal migration – people move from villages to cities, causing overpopulation of megacities (Almaty, Astana, Shymkent). The influx of migrants from neighboring countries (Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan) affects the labor market.
Changes in education: introduction of trilingual education (Kazakh, Russian, English), exchange and study abroad programs (Bolashak), growth of online education and distance technologies, introduction of artificial intelligence in the education system.
Environmental challenges and Kazakhstan. Global climate change affects Kazakhstan, causing:
- «Pustomanie» lake (south of the country, Kyzylorda region);
- melting glaciers and water scarcity (a threat to agriculture and hydropower);
- airpollution (Almaty is one of the most polluted cities in the CIS);
- the need to switch to a «green economy» (the goal is 50% of energy from renewable sources by 2050).
Technological trends and Kazakhstan in the context of globalization.
Digitalization of the economy, development of «Digital Kazakhstan» (e-government, introduction of blockchain technologies). Growth of the IT industry-fintech, startups, expansion Kaspi.kz. Development of artificial intelligence and automation.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain. Kazakhstan has become one of the world leaders in bitcoin mining after the ban on mining in China. Regulation of the crypto market and fin-tech development (Astana Hub).
Kazakhstan does not stay away from global processes:
- economic integration opens up new markets, but does not require economic diversification.
- political multi-vector approach allows balancing between the great powers;
- global challenges (ecology, urbanization, migration) require strategic solutions;
- digital transformation and technology development can become growth points for the future of Kazakhstan.
[200] Iglin A. V. The State in the Context of Globalization: Economy, Politics, Law // Scientific Review. Economic Sciences. – 2016. – No.6. – Pp. 65–74; URL: https://science-economy.ru/ru/article/view?id=858 (Date of access 17.03.2025)
[201] Same reference.
[202] Peters V. G. Globalization, Governance, and Its Institutions // Otechestvennye Zapiski. – 2004. – No. 2 (17). – P. 83.
Fair Globalization: Creating Opportunities for All / World Commission on the Social Dimensions of Globalization. – Geneva: ILO Publishing. – 2004. – P. 18.
[203] Dolgikh O. S. State and Law in the Context of Globalization // Evolution of State and Law: Problems and Prospects: Collection of Scientific Papers of the 4th International Scientific Conference. – Vol. 2. – Kursk, 2022. – Pp. 91–92.