
CHAPTER 14. PUBLIC POLICY IN THE CONTEXT OF GLOBALIZATION AND CRISES
14.4 The role of international organizations and supranational regulation in solving global problems
An international organization – is a political, economic, commercial or any other union of different states of the world, which is based on an agreement and is aimed at solving various international problems.
Globalization, on the other hand – is the integration of global economies, cultures, and societies around the world. Its essence lies in the growing connection of states, companies and societies of different countries from each other. It already follows from the definitions that the role of international organizations in the process of globalization is enormous. They are the driving factor of its development, maintenance and operation.
International organizations connect different spheres of societies around the world, supporting the process of globalization. Also, for example, various trade organizations play the role of a regulator of different economic relations that arise and interpenetrate each other, which is the main factor of globalization. International organizations prevent the emergence of new challenges and threats from new participants in the growing process of globalization, for example, African countries. They control the spread and problems caused by the initial stages of globalization in these countries, help them «fit into the market», due to their international economic weakness in the global market, as well as the integration of international culture into their societies.
In the modern world, international organizations are the main organizer of communication between states. International organizations (International organizations) is an association of States in accordance with international law and on the basis of an international treaty for cooperation in political, economic, cultural, scientific, technical, legal and other fields, which has the necessary system of bodies, rights and obligations derived from the rights and obligations of States in an autonomous will, the scope of which is determined by the international law of the Russian Federation. which is determined by the will of the Member States.
In the modern world, international organizations are the main organizer of communication between its states.
An international organization –is an association of States in accordance with international law and on the basis of an international treaty for cooperation in political, economic, cultural, scientific, technical, legal and other fields, which has the necessary system of bodies, rights and obligations derived from the rights and obligations of States, political will, the scope of which is determined by the will of the member States. Modern international organizations are divided into two main types: intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations. The role of both is significant and they all contribute to the communication of states in various spheres of life. But still, these two types have their own characteristics.
Any intergovernmental organization must have at least six characteristics.
First, it is created in accordance with international law. This is the most significant feature that is crucial. Any governmental organization should be established on a legitimate basis, namely, the organization should not infringe on the interests of an individual State and the international community as a whole. In addition, any international organization is created on the basis of an international treaty (convention, agreement, treaty, protocol, etc.). The parties to such a treaty are sovereign states, and in recent years, intergovernmental organizations are also participants in international organizations. For example, the EU is a member of many international fishing organizations.
The goal of creating any international organization is to unite the efforts of states in one or another area: political (OSCE), military (NATO), economic (EU), monetary and financial (IMF) and others. But an organization like the UN should coordinate the activities of States in almost all areas. In such a case, the international organization acts as an intermediary between the member States. Sometimes States refer the most complex issues of international relations to organizations for discussion and resolution[204].
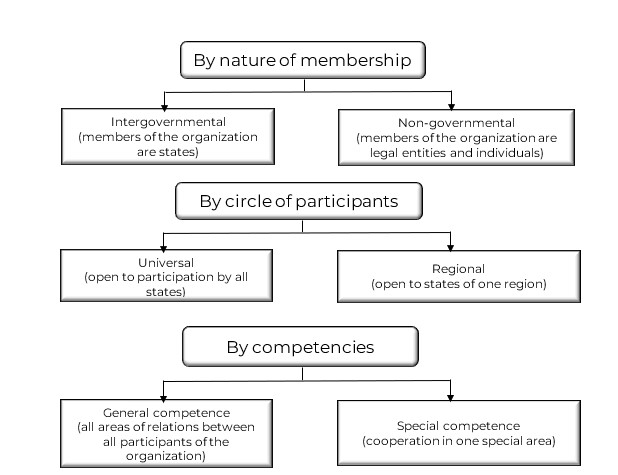
Figure 14.4.1 – Classification of international organizations
The most important international organization is the UN.
It was established in 1945 in San Francisco to maintain international peace and security after the League of Nations proved ineffective and unable to prevent World War II.
The phrase «United Nations» was first used by Franklin Roosevelt in reference to the Allied Countries. It was then used in the «Declaration of the United Nations», signed by twenty-six countries on January 1, 1942, calling for the continuation of the struggle against the Triple Alliance (Rome, Berlin, Tokyo).
A key aspect of the Organization's creation is the development of the UN Charter, which was signed on June 26, 1945 and ratified on October 24, 1945 by 50 countries, which marked the beginning of the United Nations.
The UN headquarters is located in New York on a plot of land donated by John Rockefeller, and now its offices can be found all over the world, including ball complexes in Geneva and Vienna.
The UN Charter sets out its objectives, as approved by the Member States at the time of signing:
- to maintain international peace and security and, to this end, to take effective collective measures to prevent and eliminate threats to the peace and to suppress acts of aggression or other violations of the peace, and to conduct by peaceful means, in accordance with the principles of justice and international law, the settlement and settlement of international disputes or situations that may lead to a breach of the peace;
- to develop friendly relations between nations based on respect for the principle of equal rights and self-determination of peoples, as well as to take other appropriate measures to strengthen universal peace;
- to carry out international cooperation in solving international problems of an economic, social, cultural and humanitarian character and in promoting and encouraging respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms for all peoples, without distinction as to race, sex, language or religion;
- to be a center for coordinating the actions of nations and achieving these common goals.
To achieve these goals, the UN and its Members act in accordance with the following principles:
- The organization is based on the principle of sovereign equality of allits Members;
- In the Council of Europe, the Members of the United Nations faithfully fulfill their obligations under the Charter in order to ensure that they all have the rights and benefits resulting from membership in the Organization.
- In the Council of Europe, Members of the United Nations resolve their international disputes by peaceful means so as not to endanger international peace and security and justice.
UN structure.
The General Assembly. It occupies a central position as the main deliberative, decision-making and representative body. The General Assembly considers the principles of cooperation in the field of international peace and security; elects non-permanent members of the UN Security Council, members of the Economic and Social Council; appoints the UN Secretary-General on the recommendation of the Security Council; elects members of the International Court of Justice jointly with the Security Council; coordinates international cooperation in the economic, social, cultural and humanitarian spheres; and performs other functions. Powers provided for in the UN Charter.
The secretariat. This is an international staff working in institutions around the world and performing a variety of day-to-day work of the Organization. It serves the other principal organs of the United Nations and implements their programs and policies. The UN Secretary-General heads the Secretariat.
General Secretary. The Secretary-General, who is appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a 5-year term with the possibility of re-election, heads the Secretariat.
International Court of Justice. The main judicial body of the United Nations. The Court is composed of 18 independent judges acting in their personal capacity and not representing the State. Only the state can be a party to the case of this Court, and legal entities and individuals do not have the right to apply to the Court.
Economic and Social Council. Performs the functions of the United Nations in the field of economic and social international cooperation.
The Custody Council. The Trusteeship Council suspended its work on 1 November 1994 after the last remaining UN Trust Territory, Palau, gained independence on 1 October 1994.
Specialized institutions. According to the UN Charter, any principal organ of the United Nations may establish various subsidiary bodies to carry out its duties. The most famous of them are: the World Bank, the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), UNESCO.
The Security Council. It has the primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security; all UN members must take its decisions. The five permanent members of the Security Council (the Russian Federation, the United States, the United Kingdom, France, and China) have the right of veto. The Permanent Representative of Russia to the UN represents Russia. The Security Council consists of 15 members: five members of the Council are permanent (Russia, the United States, Great Britain, France and China), the remaining ten members (in the terminology of the Charter – «non-permanent») are elected to the Council in accordance with the procedure provided for in the Charter.
The United Nations (UN) has 193 Member States. The last State to join was South Sudan in 2011. In addition, two States have observer status at the UN: the Holy See (Vatican City) and the State of Palestine.
In a situation where the role of regulating international relations at the multilateral level is increasing, the participation of international organizations in such regulation is becoming more diverse. Objectively, the UN plays the most active role in this regard. At the present stage, international organizations have become centers for uniting the efforts of States to develop new forms of cooperation in the political and economic sphere.
Global economic and social organizations.
The creation of international organizations and their development took place in stages. Gradually, the states realized the need for international cooperation in various spheres of life, which led to the exchange of inventions in the field of science, military equipment, and art. The international organizations of the past became the prototypes of modern international organizations, which are now numerous and play an important role in modern international relations.
Political and multifunctional organizations.
Modern international organizations are divided into three main types: intergovernmental (interstate), non-governmental organizations and transnational corporations. Their role is significant and they all contribute to the communication of States in various spheres of life. But still, each of these types has its own characteristics, signs.
An international intergovernmental organization (IMHO) is an association of States established on the basis of a treaty to achieve common goals, having permanent bodies and acting in the common interests of Member States, while respecting their sovereignty.
MMOs can be classified as:
- a) on the subject of activity-political, economic, credit and financial, trade, health care, etc.;
- b) in terms of participants – universal (i.e. for all states – UN) and regional (Organization of African Unity);
- c) according to the order of admission of new members – open or closed;
- d) by field of activity – with general (UN) or special competence (UPU);
- e) according to the goals and principles of the activity-lawful or illegal;
- f) by the number of members – global (UN) or group (WHO).
Non-governmental organizations.
International non-governmental organizations (INGO) – any international organization that is not established on the basis of an intergovernmental agreement, which is not created on the basis of an interstate agreement and unites individuals or legal entities. Such organizations must be recognized by at least one State, but operate in at least two States. Similar organizations are created on the basis of a constituent act.
International non-governmental organizations (INGS) play an active role in all aspects of modern international relations. In a number of areas, they are even leaders, for example, the Committee of the Red Cross, whose principles of activity are humanity, impartiality, independence and voluntariness, has made a great contribution to the interaction of States in various fields.
Transnational corporations (TNCs) – are engaged in purely economic activities, but try to influence not only the economy, but also the policy of states.
International organizations cover a wide variety of aspects of international relations. They are created in the economic, political, cultural, and national fields. They have certain features and specifics:
- Regional organizations such as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, the European Economic Community, the League of Arab States, and others;
- Organizations of an economic nature that cover finance, trade, and so on, such as the International Chamber of Commerce, the International Monetary Fund, and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
- organizations in the field of certain branches of the world economy, for example: the International Energy Agency, the International Atomic Energy Agency, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries;
- Political and economic organizations, for example: Organization of African Unity;
- Professional organizations: International Organization Of Journalists, International Organization Of Criminal Police;
- Demographic organizations: International Democratic Federation of Women, World Youth Association;
- Cultural and sports organizations: International Olympic Committee, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization;
- Military organizations: North Atlantic Treaty Organization, Pacific Security Pact;
- Trade union organizations: International Confederation of Free Trade Unions, World Confederation of Labor;
- Various organizations in support of peace and solidarity: World Peace Council, Pagoush Movement, International Peace Institute;
- Religious organizations: World Council of Churches, Christian Peace Conference;
- International Red Cross – an organization whose goal is to help prisoners of war, victims of war, disasters and natural disasters;
- Environmental organizations: Greenpeace, etc.
In the modern world, it is with the help of international organizations that cooperation between States is carried out. International organizations not only regulate interstate relations, but also make decisions on global issues of our time.
The creation and existence of international organizations opens up wider opportunities for bringing all mankind closer together and contributes to the rapid development of civilization[205].
[204] Narmatova N. B. The Role of International Organizations in Integration Processes. Science and New Technologies. – No.6, 2012. http://www.science-journal.kg/media/Papers/nntiik/2012/6/nntiik-2012-N6-139-141.pdf (Date of access: 26.03.2025)
[205] International Organizations in the Global Political Process. https://textbook.tou.edu.kz/books/117/13.html (Date of access: 26.03.2025)